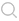【導讀】磁飽和是磁性材料的一種物理特性,指的是導磁材料由于物理結構的限制,所通過(guò)的磁通量無(wú)法無(wú)限增大,從而保持在一定數量的狀態(tài)。一般的電感都有一條磁化曲線(xiàn)(B-H Curve), 這是一條反應磁場(chǎng)強度H和磁感應強度B的一條對應曲線(xiàn)。
當磁場(chǎng)強度 H 增加時(shí),磁感應強度 B 逐漸趨于一個(gè)最大值,即為該物質(zhì)的飽和度。事實(shí)上,飽和之后,磁感應強度 B 也在逐漸增加,但比達到飽和度前的增長(cháng)速率小了3個(gè)數量級。
磁場(chǎng)強度 H 和磁感應強度B的關(guān)系可以用磁導率,或相對磁導率表達,當中的是真空磁導率。磁性金屬的磁導率不是一個(gè)恒定不變的量,而是取決于磁場(chǎng)強度 H 。在可飽和的金屬中,相對磁導率隨磁場(chǎng)強度 H 的增加達到一個(gè)最大值,然后隨著(zhù)它的飽和發(fā)生轉變再減小。也就是說(shuō), 當磁場(chǎng)強度H達到一定程度的時(shí)候,因為感應強度B飽和原因,磁導率會(huì )越來(lái)越小,易導致電感值越來(lái)越小(電感值與磁導率成正比).
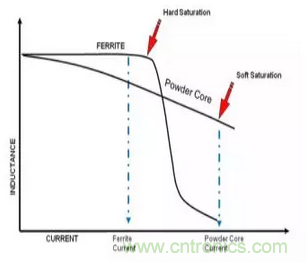
所以一般電感的電感值在0A電流的時(shí)候電感值最大,但是隨著(zhù)電流增大電感值會(huì )慢慢下降,不同的磁芯材料,電感值的下降速度不一樣。當電感值下降很快的時(shí)候,我們稱(chēng)這個(gè)電感為Soft Saturation, 當電感值開(kāi)始下降很慢的時(shí)候,我們成為Stiff/Hard Saturation。不少電感值在飽和后,只有原電感值的1/3,甚至1/10。這點(diǎn)變化也是電路設計中需要重點(diǎn)考慮的。